Tetrazolium violet is a tetrazolium salt and has been proposed as an antitumor agent. In this study, we reported for the fi rst time that tetrazolium violet not only inhibited human lung cancer A549 cell proliferation but also induced apoptosis and blocked cell cycle progression in the G1 phase. The results showed that tetrazolium violet signifi cantly decreased the viability of A549 cells at 5-15μM. Tetrazolium violet -induced apoptosis in A549 cells was confi rmed by H33258 staining assay. In A549, tetrazolium violet blocked the progression of the cell cycle at G1 phase by inducing p53 expression and further up-regulating p21/WAF1 expression. In addition, an enhancement in Fas/APO-1 and its two forms of ligands, membrane-bound Fas ligand (mFasL) and soluble Fas ligand (sFasL), as well as caspase, were responsible for the apoptotic effect induced by tetrazolium violet. The conclusion of this study is that tetrazolium violet induced p53 expression which caused cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. These fi ndings suggest that tetrazolium violet has strong potential for development as an agent for treatment lung cancer.
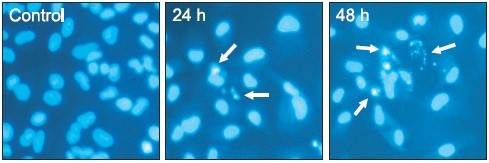
Fig. 3. TV-induced morphological changes of A549 cells. Morphological
changes of A549 cell nuclei were observed by fl uorescence
microscopy. The cells were stained with Hoechst 33258 to identify
apoptotic cells. Some of the condensed and fragmented nuclei are
indicated by arrows. Data are representative of three independent
experiments with similar results.
Additional Information:
1. Author Information:Xiao-Hong Zhang, Nan Zhang, Jian-Mei Lu, Qing-Zhong Kong and Yun-Feng Zhao
Correspondence: E-mail:zhaoyf1989@yahoo.com.cn
2. Published : Biomol Ther 20(2), 177-182 (2012)
1. Author Information:Xiao-Hong Zhang, Nan Zhang, Jian-Mei Lu, Qing-Zhong Kong and Yun-Feng Zhao
Correspondence: E-mail:zhaoyf1989@yahoo.com.cn
2. Published : Biomol Ther 20(2), 177-182 (2012)
