MMPT, (5-[(4-methylphenyl)methylene]-2-(phenylamino)-4(5H)-thiazolone), a thiazolidin compound, was identified in our laboratory as a novel antineoplastic agent with a broad spectrum of antitumor activity against many human cancer cells. A previous study showed that MMPT inhibited cell growth, and induced apoptosis in H1792 cells. In this study, the antiproliferative activity of MMPT was investigated. The results showed that MMPT was able to inhibit A549 cell growth in a time- and dose-dependent manner by blocking cell cycle progression in the G2 phase and inducing apoptosis. MMPT induced DNA fragmentation and caspase activation in A549 cells, both of which are hallmarks of apoptosis. The apoptotic process was accompanied by the generation of reactive oxygen species, depletion of glutathione (GSH), and reduction the GSH/GSSG ratio, suggesting that MMPT may induce apoptosis in A549 cells through a reactive oxygen species dependent pathway. Treatment with a thiol antioxidant, NAC, showed the recovery ofGSH depletion and the reduction of reactive oxygen species levels in MMPT-treated cells, which were accompanied by the inhibition of apoptosis. In contrast, L-buthionine sulfoximine (BSO), a well-known inhibitor of GSH synthesis, aggravated GSH depletion and cell death inMMPTtreated cells. In conclusion,we have demonstrated thatMMPT inhibits the growth of A549 cells by inducing a G2 arrest of the cell cycle and by triggering apoptosis accompanied with the depletion of GSH.
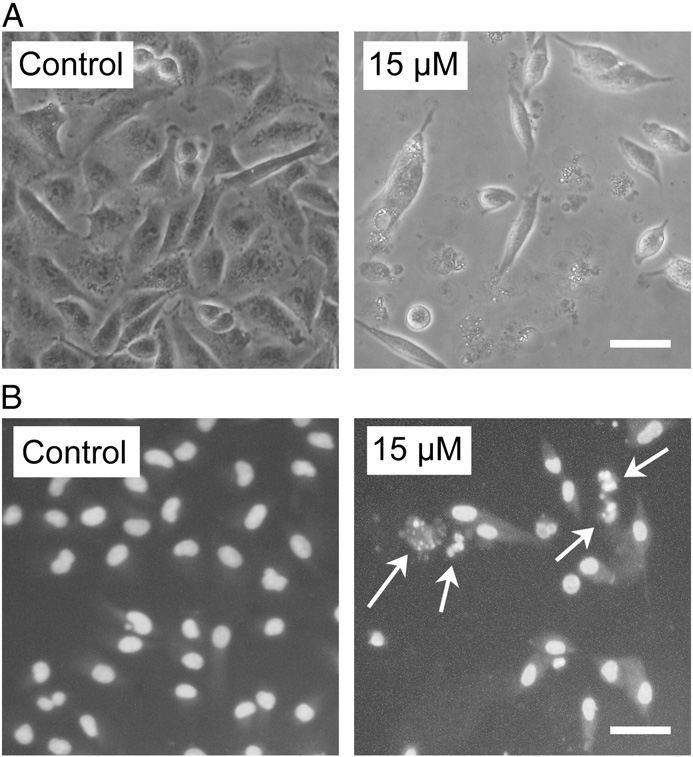
Fig. Effects ofMMPT on apoptosis in A549 cells. Exponentially growing cellswere treated
with the indicated concentrations of MMPT for the indicated times.
Additional Information:
1. Author Information:Yun-feng Zhao, Cui Zhang, You-rui Suo
Correspondence: E-mail:zhaoyf1989@yahoo.com.cn
2. Published : European Journal of Pharmacology 688 (2012) 6–13
