Hirsutella sinensis, the anamorph of Ophiocordyceps sinensis (syn. Cordyceps sinensis), is a great substitute for precious and rare wild Cordyceps sinensis to effectively treat a variety of lung and kidney diseases. In this study, an α-glucan (named as HSWP-2a) was obtained by hot water extraction, DEAE-cellulose separation, and Sepharose CL-6B purification from H. sinensis mycelia. Different from known α-glucans, HSWP-2a is an α-(1 → 4)-D-glucan that branched at O-6, O-3, or O-2 with a terminal 1-linked α-D-Glcp as side chain, with an average molecular weight of 870.70 kDa. Immunological tests showed that HSWP-2a could remarkably enhance the phagocytosis of macrophages and increase the production of NO, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, via activating the p38, JNK, and NF-κB signaling pathways. Moreover, HSWP-2a could significantly promote splenic lymphocyte proliferation. Taken together, HSWP-2a may be potentially utilized as a natural immunomodulatory agent.
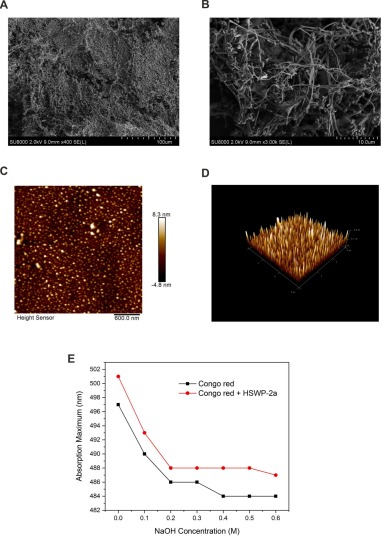
Fig. 4. (A: 400×; B: 3000×) SEM images of HSWP-2a. (C: Two-dimensional; D: Three-dimensional) AFM images of HSWP-2a. (E) Congo red assay of HSWP-2a. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
This result was published in International Journal of Biological Macromolecules with the title of “Structure and immunomodulatory activity of a water-soluble α-glucan from Hirsutella sinensis mycelia”.
The link below will guide you to the reading:
