If and how eutrophication influences the persistent soil seed bank is poorly understood. It was assumed that eutrophication could indirectly change the composition of the soil seed bank through changes in soil characteristics, aboveground plant communities and productivity, and that continuous changes in the seed bank would in turn affect the composition of aboveground plants.
Members of Key Laboratory of Restoration Ecology for Cold regions laboratory in Qinghai including postdoctoral chun-hui zhang, associate professor Buqing Yao, researcher xin-quan zhao and hua-kun zhou ,assistant professor Zhen Ma, cooperated with the scientists from American, Hungary and Lanzhou university, discussed and verified above-mentioned hypotheses by experiment on nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization in alpine meadow of eastern qinghai-tibet plateau for 9 years.
It was found that long-term application of nitrogen and phosphorus could indirectly affect the soil seed bank by changing soil PH, vegetation composition and annual net primary productivity (ANPP). However, compared with the change of vegetation composition, the composition change of soil seed bank is relatively small and stable.
The change of soil seed bank has no direct feedback to vegetation composition. Researches further emphasized the regulation function from soil PH, ANPP and vegetation to soil seed bank, highlighted the long-term stability of soil seed bank under the background of eutrophication and its important contribution to the alpine meadow ecosystem sustainability, stability of alpine grassland ecosystem and the understanding of the restoring force mechanism is of great significance.
The result was published online in March 2019, and it is titled "Direct and indirect effects on the stability of the persistent seed bank." The research was funded by Key Laboratory of Restoration Ecology for Cold regions laboratory in Qinghai, "Qinghai innovation platform construction project", the national key research and development plan, "restoration technology and demonstration of degraded alpine ecosystem in Three-river-source region", the national natural science foundation of China, Qinghai natural science foundation and other projects.
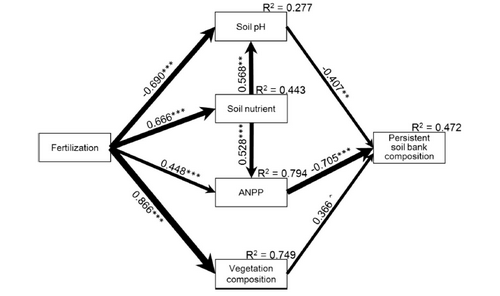
The results of final structural equation modeling showing the causal relationships among fertilization, soil nutrient, soil pH, ANPP, vegetation composition, persistent soil bank composition.
