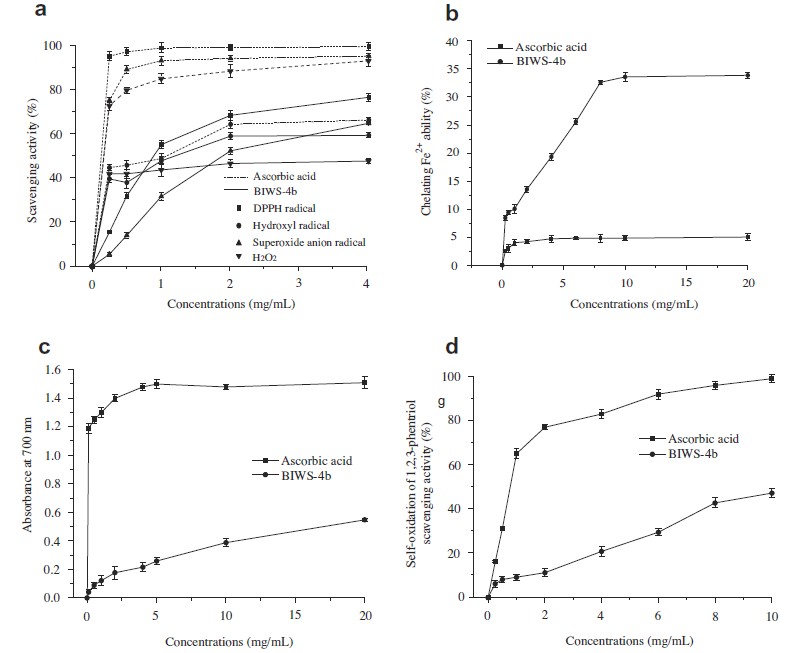
The non-lichenized ascomycete Bulgaria inquinans (Fries), growing in the Changbai Mountain of China, has been used as medicinal diet for many years. In a previous study, we have reported that a heteropolysaccharide BIWS-4b from the fruit bodies of B. inquinans (Fries) exhibited markedly antimalarial and immunostimulating activities. In this paper, the structural features and antioxidant activity of BIWS-4b were investigated. The results showed that BIWS-4b contains an α-(1→2), (1→6)-mannan core to which the glucogalactan chains are attached. The glucogalactan chains were composed of (1→6)-,(1→5)- and (1→5,6)-linked β-Galf, (1→4)-linked and non-reducing terminal β-Glcp units, and might be attached to the mannan core at the O-2 positions of α-Manp units. The antioxidant assays showed that BIWS-4b exhibited good activities, including free radicals scavenging effects, ferrous ion-chelating ability and reducing power. Thus, BIWS-4b could be used as a natural antioxidant agent for food and pharmaceutical industries.
Additional Information:
1. Author Information:
Hongtao Bi, Tingting Ga, Zonghong Li, Li Ji, Wei Yang, B. Jeff Iteku, Enxu Liu, Yifa Zhou
Correspondence: E-mail: zhouyf383@yahoo.cn, zhouyf383@nenu.edu.cn (Y. Zhou)
2. Publication History: Food Chemistry 138 (2013) 1470–1475
1. Author Information:
Hongtao Bi, Tingting Ga, Zonghong Li, Li Ji, Wei Yang, B. Jeff Iteku, Enxu Liu, Yifa Zhou
Correspondence: E-mail: zhouyf383@yahoo.cn, zhouyf383@nenu.edu.cn (Y. Zhou)
2. Publication History: Food Chemistry 138 (2013) 1470–1475
