A sensitive and efficient method using a semi-automated pretreatment device, pre-column derivatization, multivariate optimization and high performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence and mass spectrometric detection was developed and validated for the systematic determination of two biophenols in four herb-related samples (medicinal herb; herbal products in tablet, capsule and oral liquid forms) and plasma samples after oral administration to rat. Only micro-sampling of 20 _L blood was needed for the analysis, and the pretreatment procedure including blood collection, derivatization by 10-ethyl-acridine- 3-sulfonyl chloride (EASC) and injection to the sampling vials was efficiently finished in 10 min with no cumbersome and complicated operation. The novel application of artificial neural network (ANN) coupled with genetic algorithm (GA) to optimization of derivatization condition was executed and compared with the classical response surface methodology (RSM). The optimal condition for derivatization was validated by multi-criteria and nonparametric tests and used successfully to achieve the higher sensitivity (limit of detection: 0.6 and 0.8 ng/mL). The limit of reactant concentration (LORC) was put forward for derivatization method for the first time, and the lower values (2.0–2.7 ng/mL) provided the guarantee for the trace detection with the micro samples (<50 _L) required. The results of validation including selectivity, sensitivity, linearity, accuracy, precision, recovery, matrix effect and stability demonstrated the advantages of this method. The pharmacokinetic study of major bioactive components salidroside and p-tyrosol in herb Rhodiola crenulata and its products was more conveniently performed in 25 min. The established method could be the sensitive and efficient alternative method for the systematic detection of bioactive components in series of drug carriers from raw herb to herbal products and to blood in medical research. And the approaches of the thorough study played the guiding role in seeking a novel analytical method.
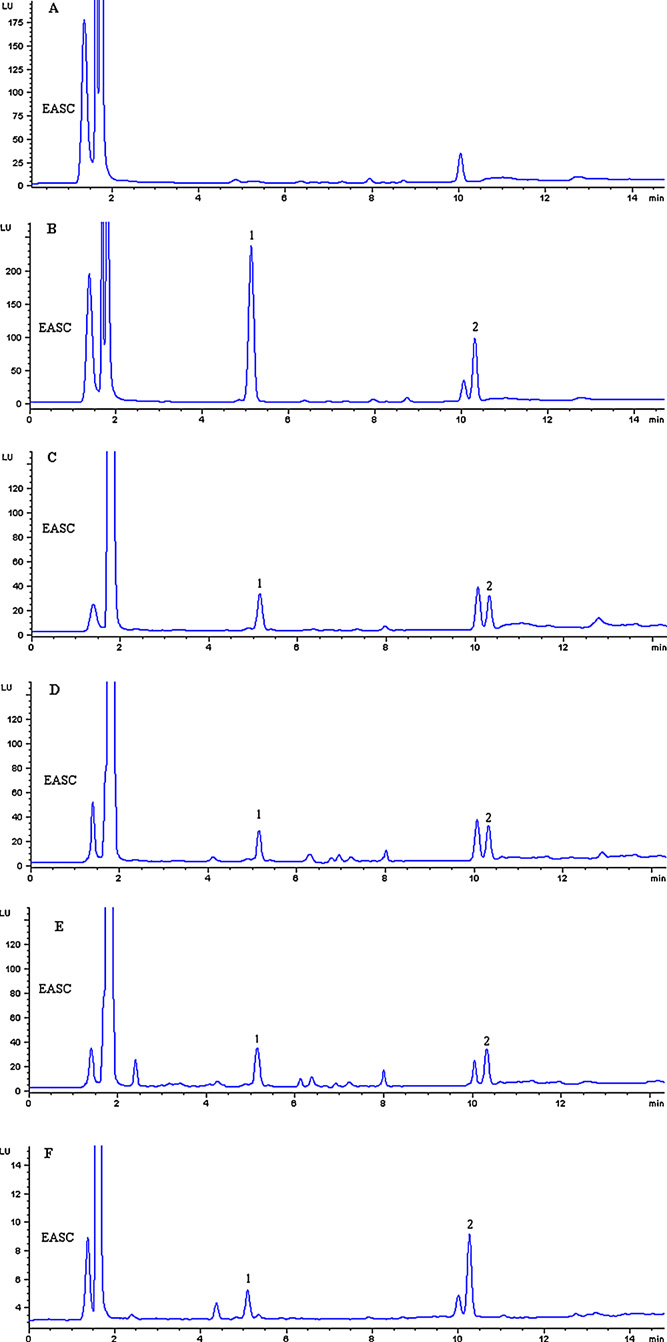
Fig. 2. The representative chromatograms for blank plasma (A), spiked blank plasma
with standard (B), and plasma samples after oral administration of Rhodiola crenulata
root (C), tablet (D), capsule (E) and oral liquid (F).
Additional Information:
1. Author Information:Guang Chen, Jun Li, Shijuan Zhang, Cuihua Song, Guoliang Li, Zhiwei Sun,Yourui Suo, Jinmao You
Correspondence: E-mail:jmyou6304@163.com
2. Published : Journal of Chromatography A, 1249 (2012)190–200
