Rapid screening of potential α-glucosidase inhibitors from the waste leaves of Rheum tanguticum by activity-oriented extraction and enrichment optimization, UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS, molecular docking and in vitro validation

August 15, 2024 In the present study, an efficient strategy has been established for rapid screening of potential α-glucosidase inhibitors from the waste leaves of Rheum tanguticum by activity-oriented extraction and enrichment opti...
Multi-omics reveal the gut microbiota-mediated severe foraging environment adaption of small wild ruminants in the Three-River-Source National Park, China
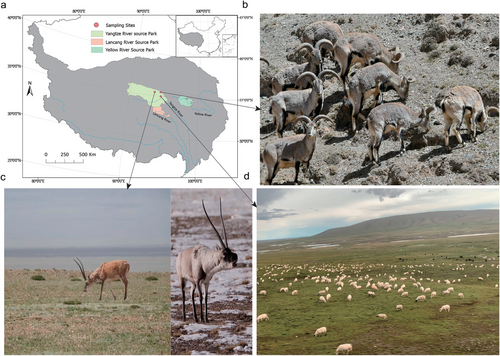
July 25, 2024 The Tibetan antelope, blue sheep, and Tibetan sheepare the dominant small ruminants in the Three-River-Source National Park.
Spatiotemporal overlap among snow leopard, bharal, and free-ranging livestock: Suggestions on mitigating human-snow leopard conflict
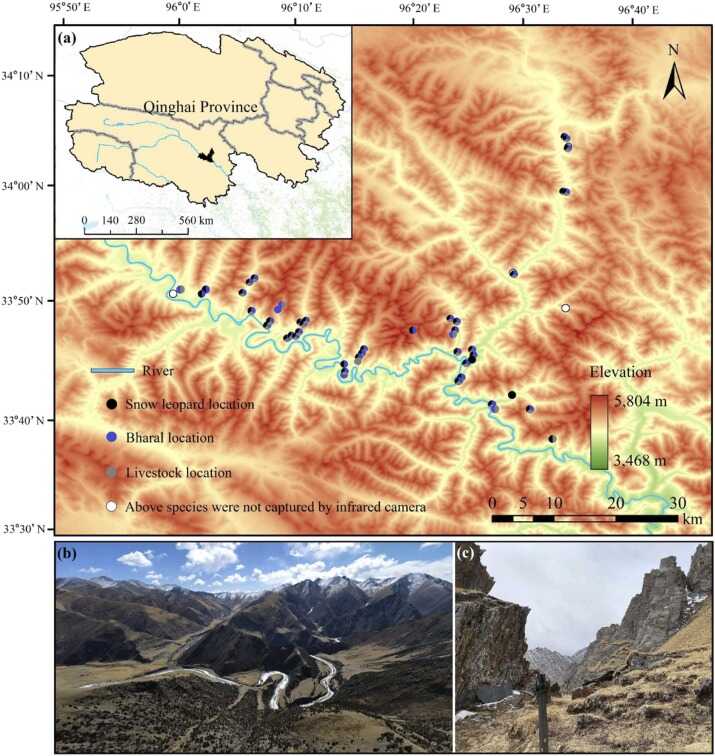
June 13, 2024 Predation on livestock by large carnivores, such as snow leopard, is a global issue that leads to human-wildlife conflicts.
Loss of PBX1 function in Leydig cells causes testicular dysgenesis and male sterility" target="_blank">Loss of PBX1 function in Leydig cells causes testicular dysgenesis and male sterility
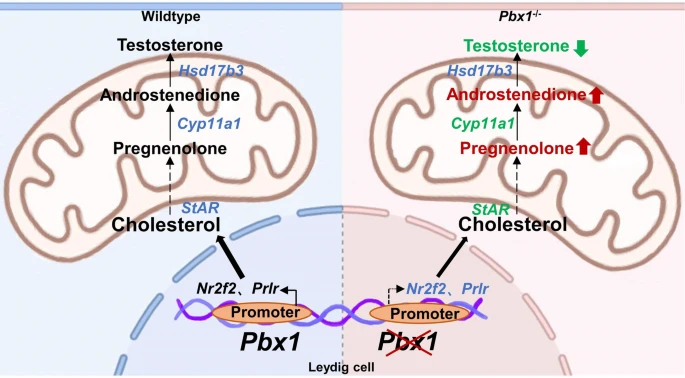
May 10, 2024 Leydig cells are essential components of testicular interstitial tissue and serve as a primary source of androgen in males.
Population genetics and ecological niche modelling shed light on species boundaries and evolutionary history of Aconitum pendulum and A. flavum
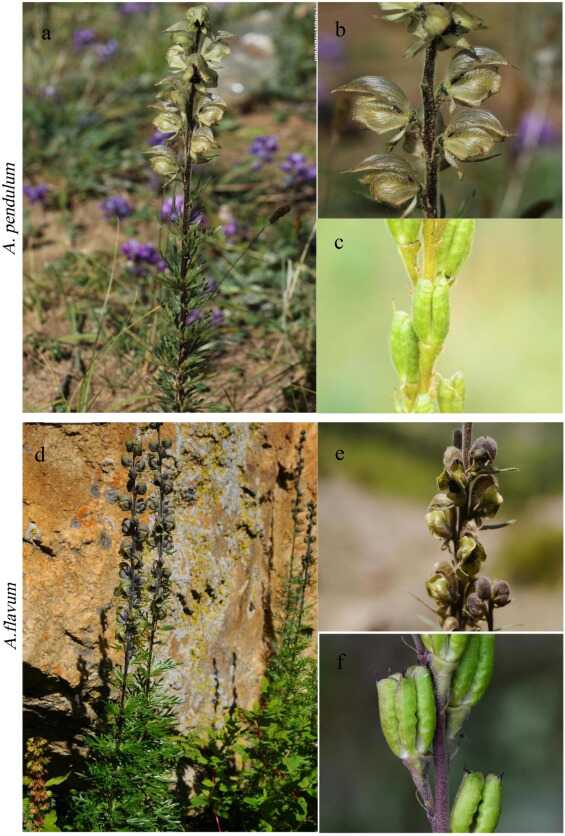

April 20, 2024 As species are fundamental units of evolutionary biology research, accurate species delimitation plays a crucial role in current biodiversity management.
