Responses of gut microbiota to altitude in a small mammal on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau
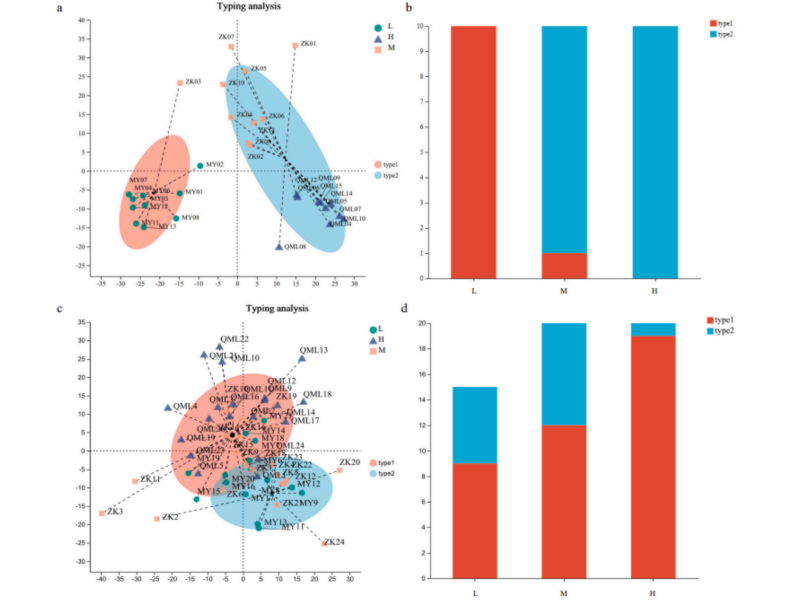
March 21, 2025 Altitude of the plateau may affect the composition and functional diversity of animal gut microbiota. However, the specific effects of altitude on the composition, community structure, and function of the host's gut m...
Multiple molecular data provide new insights into phylogeny and historical biogeography of East Asian Artemisia L. (Asteraceae)
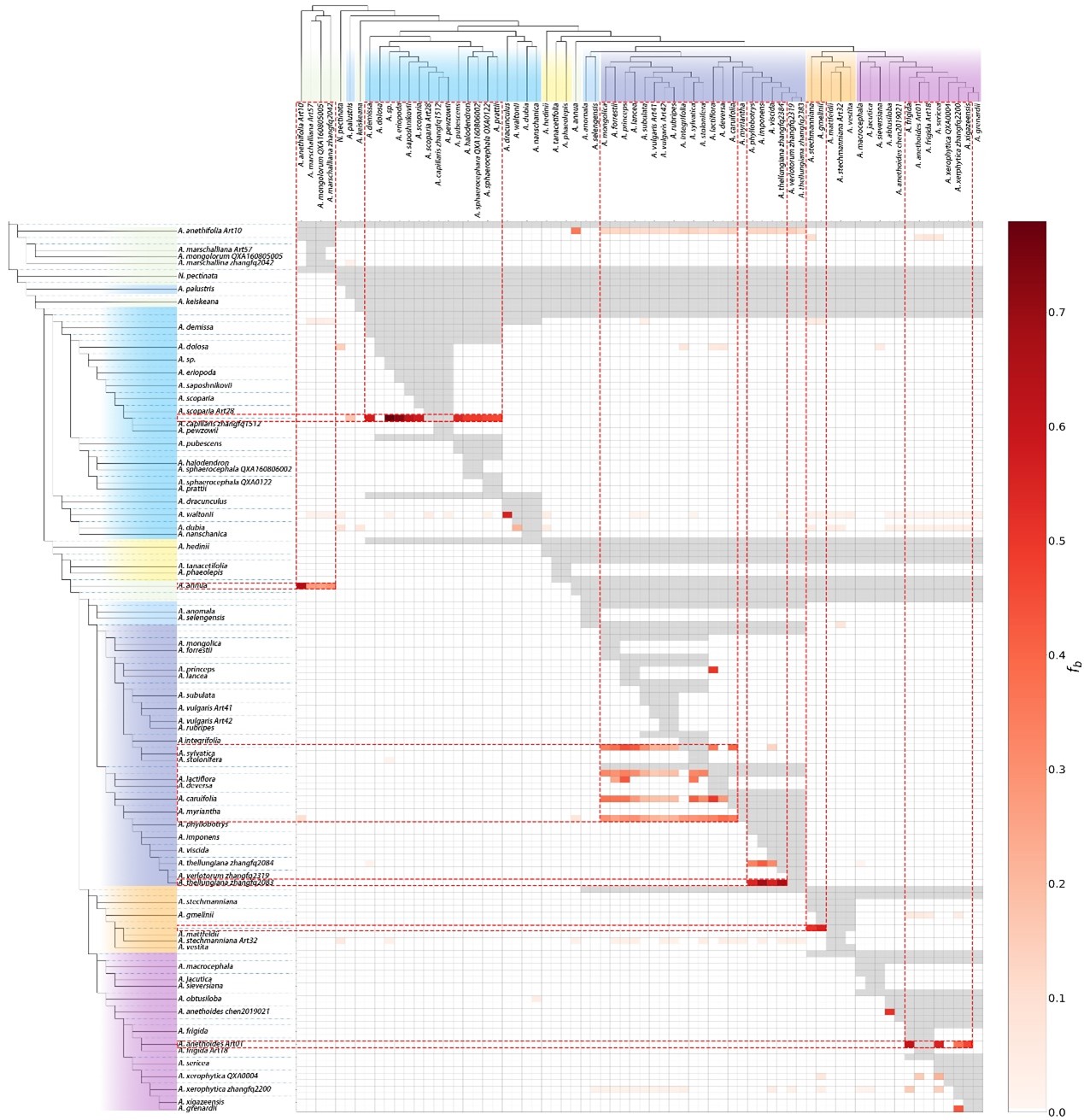
March 21, 2025 Artemisia L. is one of the most diverse genera in the Asteraceae, widely used in agriculture and medicine, with a giant range of complicated taxa. The task of establishing the phylogeny difficulties owing to the highl...
Investigating the formation and evolution of plant diversity patterns in the Qiangtang Plateau based on phylofloristics approach
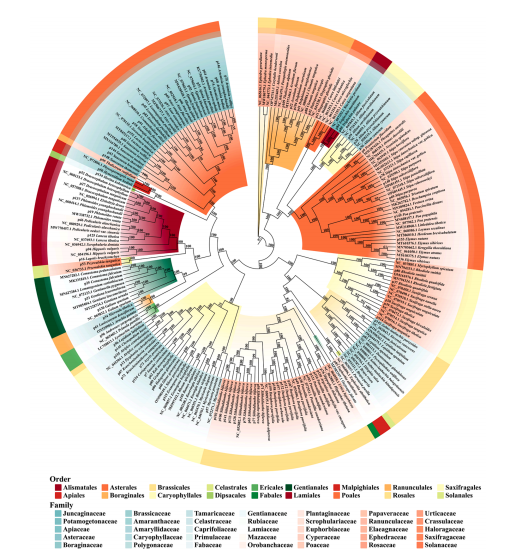
March 21, 2025 Phylofloristics integrates phylogenetic information into the analysis of flora to elucidate the origin and evolutionary history of flora. The Qiangtang Plateau, located in the hinterland of the Tibetan Plateau, is the...
Genetic structure and conservation implications of Lancea tibetica (Mazaceae), a traditional Tibetan medicinal plant endemic to the Qinghai- Tibet Plateau
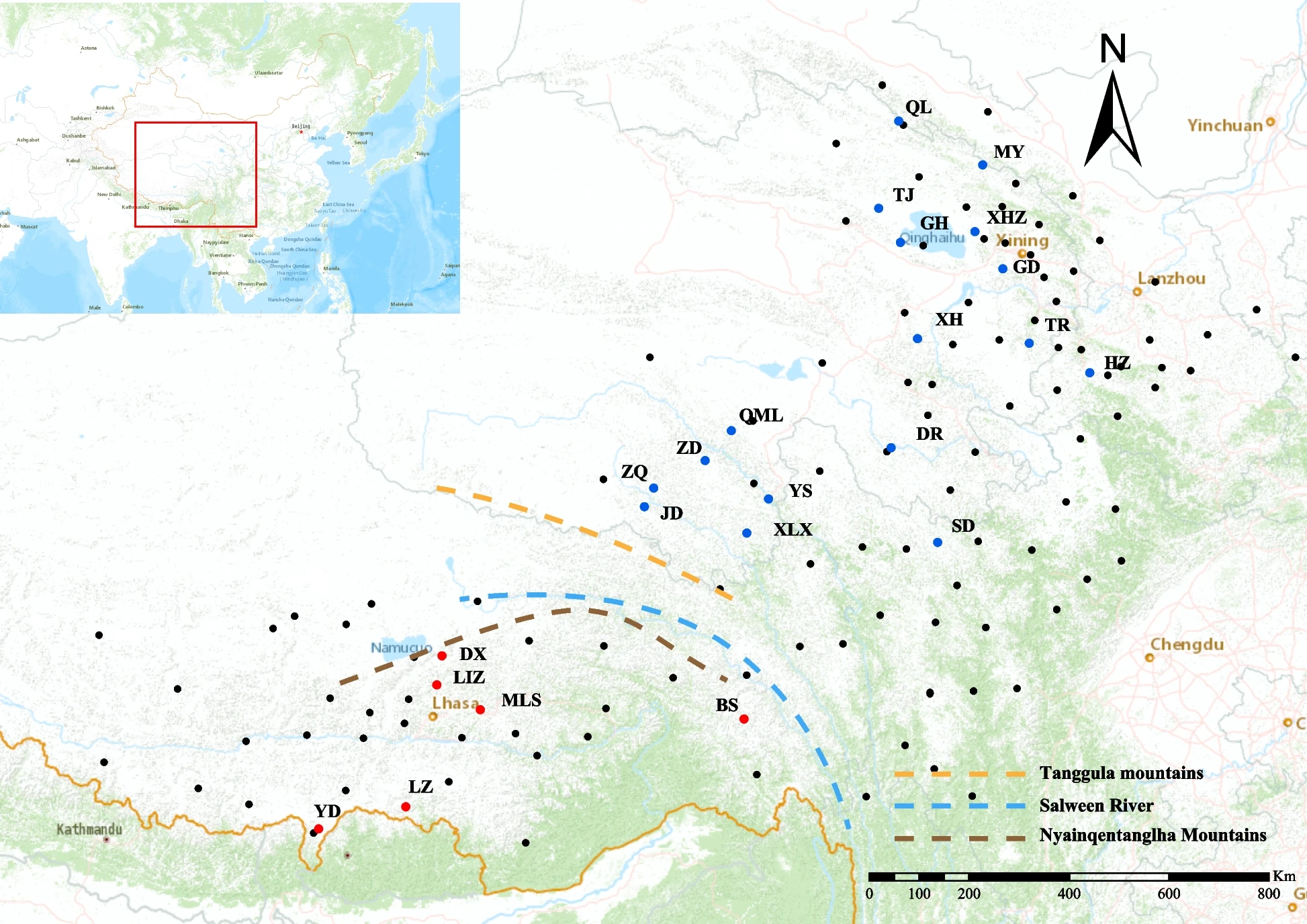
February 21, 2025 Fig.1From:Genetic structure and conservation implications of Lancea tibetica, a traditional Tibetan medicinal plant endemic to the Qinghai-Tibet PlateauThe link bellow will guide you to reading:https://doi.org/10.1186...
Underground divergence and aboveground convergence of bacterial community compositions and nitrogen cycle-related functional groups in cultivated and wild Rheum tanguticum
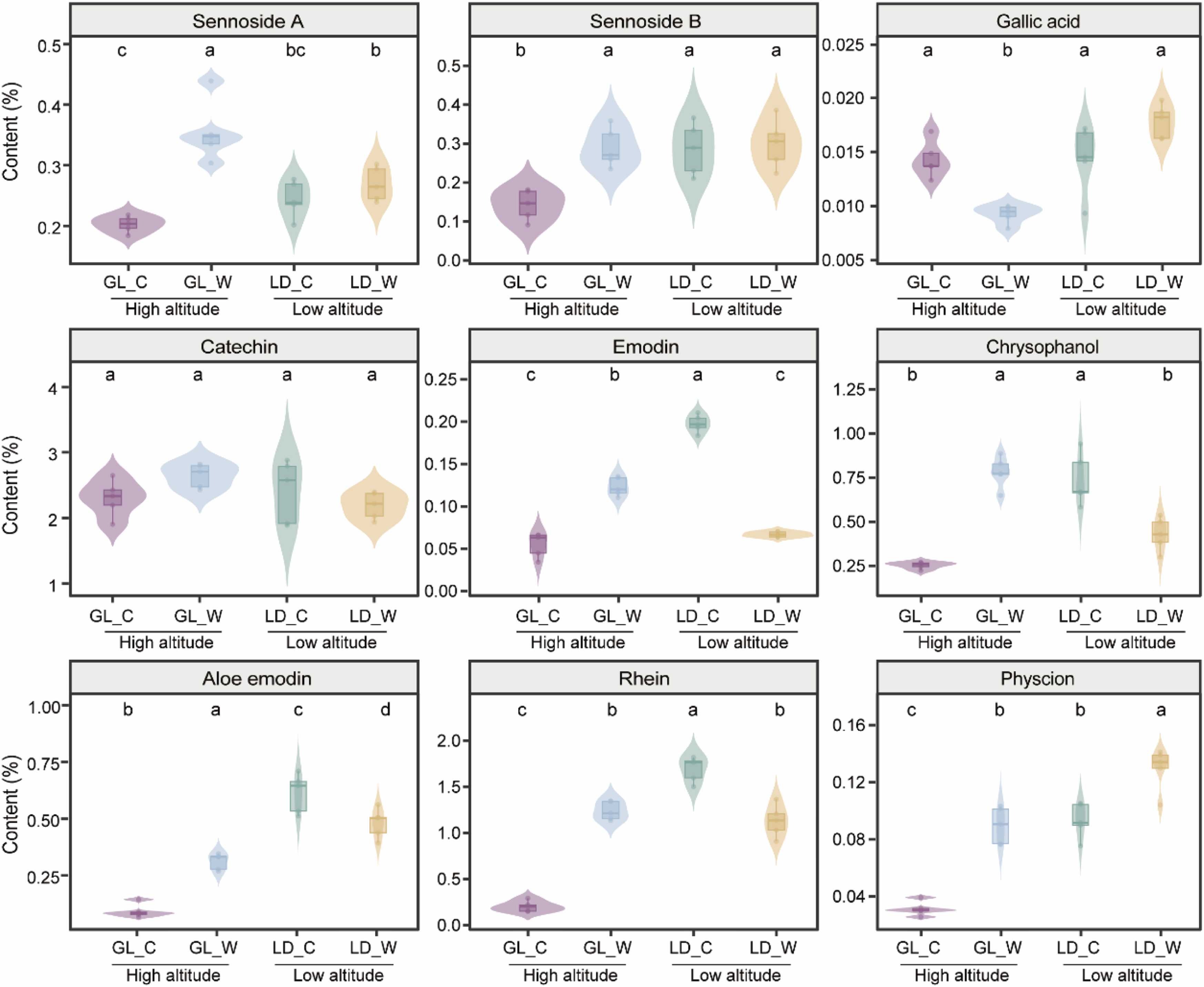
February 18, 2025 Differences in soil chemical properties resulting from fertilization may be the primary factor influencing the variation in bacterial communities between cultivated and wild soils.
