Long-term nitrogen addition of different types and levels altered the relationship between species diversity and ecosystem multifunctionality in alpine grasslands
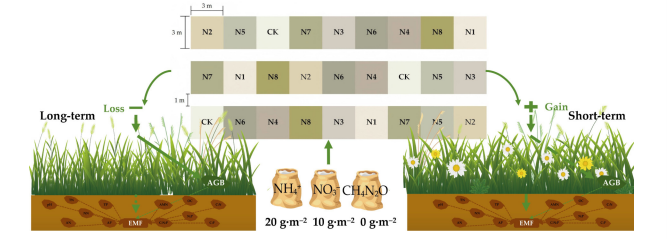
January 14, 2026 The ecological effects of nitrogen addition depend on the duration, as well as nitrogen levels and types.
Regulatory effects of soil factors and rhizosphere bacterial community composition on soil multifunctionality in Caragana korshinskii artificial plantations
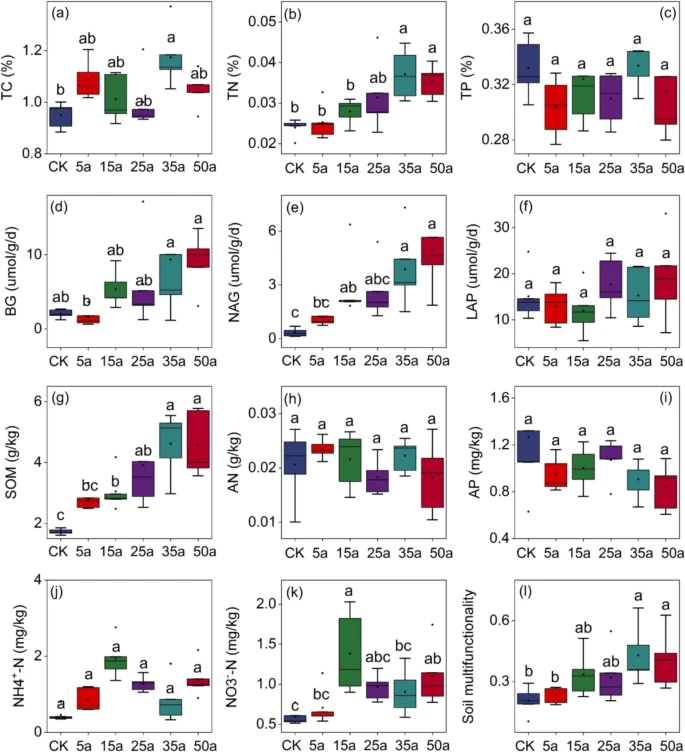
December 12, 2025 BackgroundsThe high-altitude desert ecosystem is fragile, and planting Caragana korshinskii is a key measure for ecological restoration, effectively improving soil quality, windbreak and sand fixation, and water conse...
The role of plant phenology in the response of plant productivity to decadal climate warming and cooling
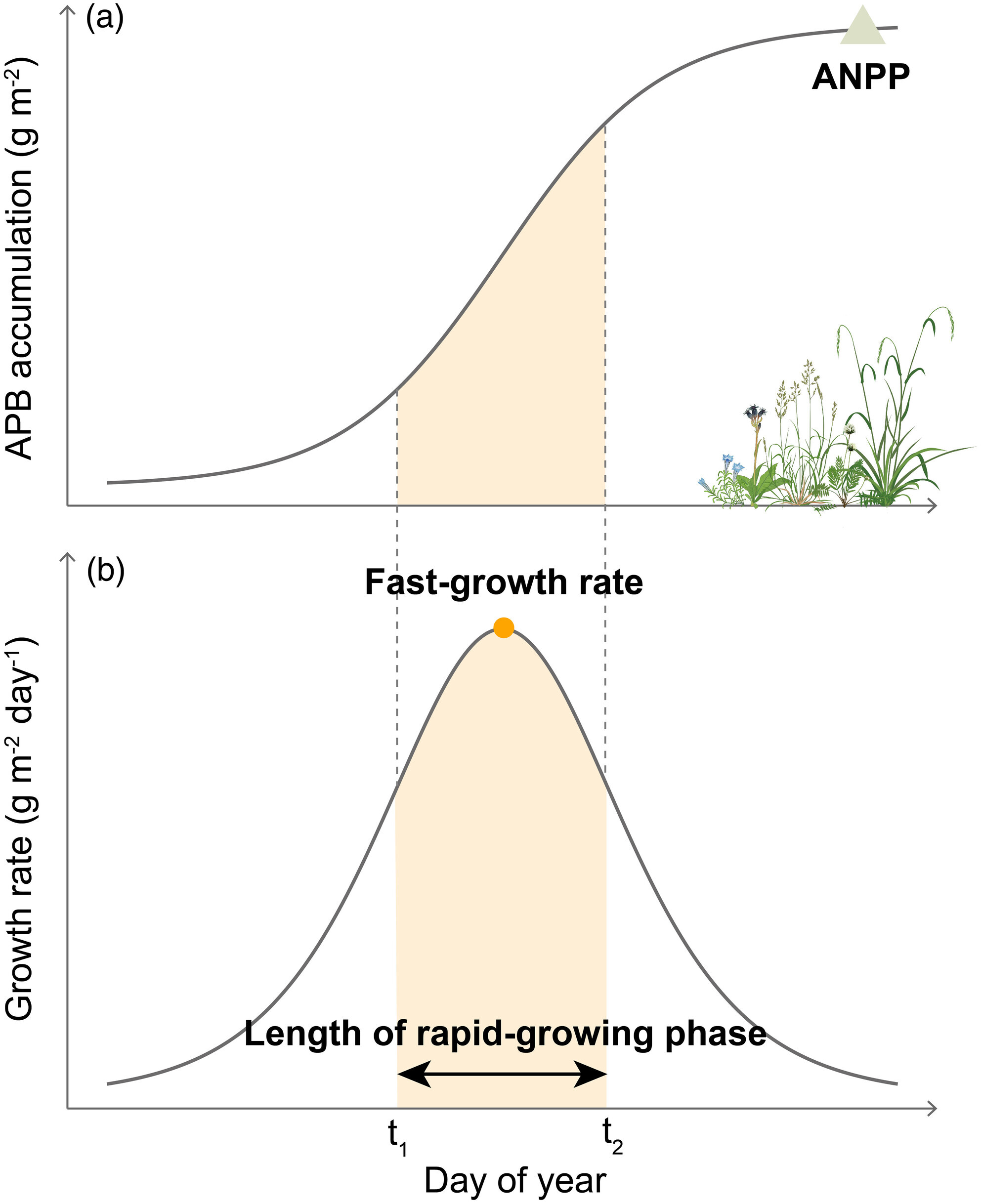
December 08, 2025 Climate change is expected to intensify over the coming decades, potentially exerting substantial impacts on above-ground net primary productivity, a key indicator of ecosystem functioning and carbon sequestration.
Grassland degradation indirectly impacts soil carbon and nitrogen by altering nematode communities in permafrost area
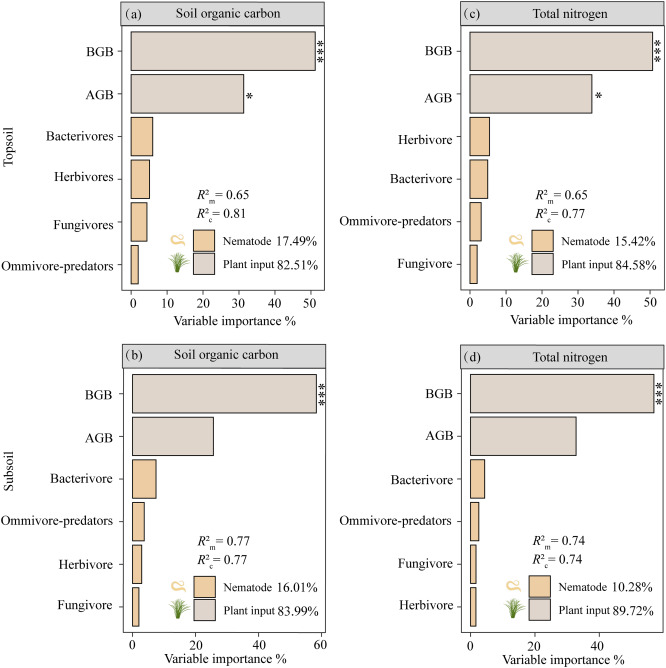
October 27, 2025 Soil nematodes play a critical role in soil nutrient dynamics through their interactions within the food web and their inherent properties.
Effects of alpine meadow degradation on soil nematode diversity and community composition on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
September 17, 2025 We evaluated soil nematode community composition and diversity as well as a range of soil physicochemical properties during alpine meadow degradation and identified the ecological predictors of soil nematode diversity...
