Mitigating Human–Large Carnivore Conflicts via Time-Regulated Management of Free-Ranging Livestock in the Sanjiangyuan Region, China
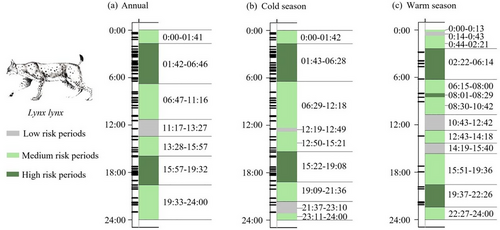
March 02, 2026 Livestock depredation by large carnivores is a global conservation challenge that fuels human – carnivore conflict and hinders coexistence with agropastoral communities.
Spatial Distribution and Key Driving Factors of Soil Potentially Toxic Elements in Sanjiangyuan Alpine Grasslands—A Dual-Factor Perspective of Natural and Anthropogenic Drivers
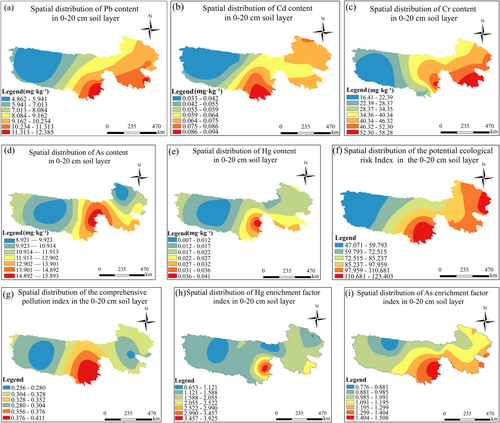
February 06, 2026 As the hinterland of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, the Sanjiangyuan region possesses pivotal ecological and strategic value, with its soil quality serving as a cornerstone for regional and global ecological balance.
Five years of re-ploughing of grass cultivation (Elymus nutans) in the eastern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau proves to management measure: An eddy covariance-based analysis
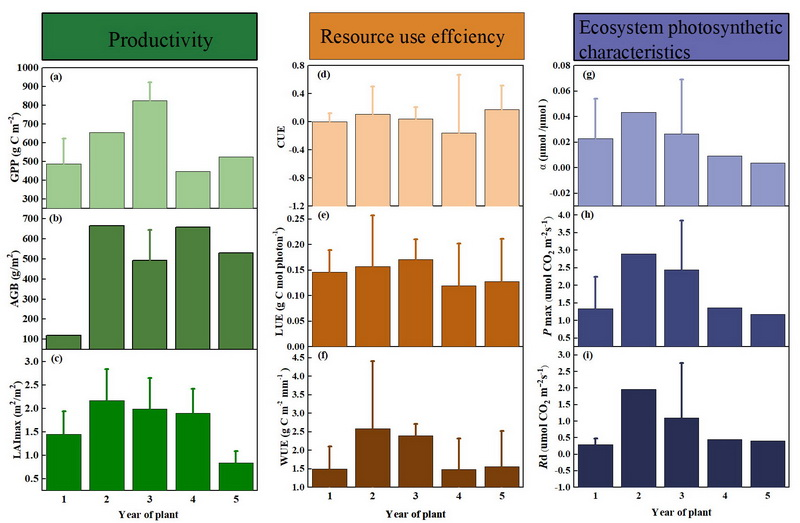
February 06, 2026 Regarding resource use efficiency, C use efficiency remained relatively stable at 0.04 ± 0.013, while water use efficiency and light use efficiency displayed unimodal dynamics.
Differences in Dietary Composition and Interspecific Competition Among Large Carnivores on the Qinghai–Xizang Plateau
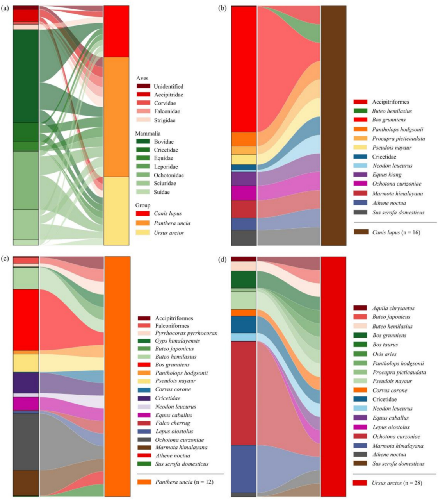
February 05, 2026 Understanding and quantifying the dietary composition of large carnivores is crucial for elucidating their functional roles within ecosystems including their top–down regulation of prey populations and their interact...
Dynamic regulation of spermatogenesis and hybrid sterility revealed by single-cell analysis in yak and cattle
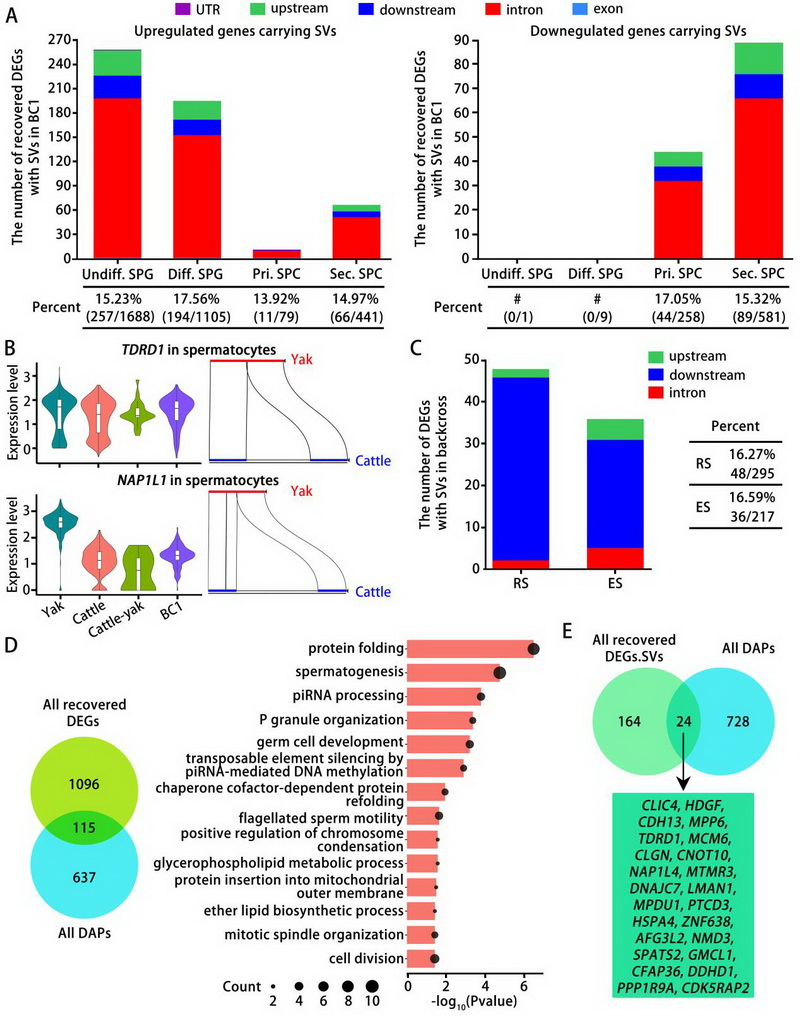
February 02, 2026 Spermatogenesis is a highly orchestrated germ cell differentiation process involving the dynamic regulation of cell fate transitions. Dissecting the molecular landscapes of spermatogenic cell types is crucial for iden...
